Ivervid 3mg is an anthelmintic medication containing Ivermectin as the active ingredient. Ivermectin binds to glutamate-gated chloride channels in the nerve and muscle cells of the parasite that results into paralysis and ultimately death of a parasite. It is used to treat parasitic infections caused by roundworms, threadworms, hookworms, whipworms, pinworms, and scabies-a skin infestation.
Key Features
| About Ivervid 3 mg |
|---|
| Drug Class: Antiparasitic Agents |
| Subclass: Anthelmintics, specifically Macrocyclic lactones |
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Composition | Active ingredient: Ivermectin Inactive ingredients: • Microcrystalline cellulose • Magnesium Stearate • Titanium dioxide • Hydroxypropyl cellulose • Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) |
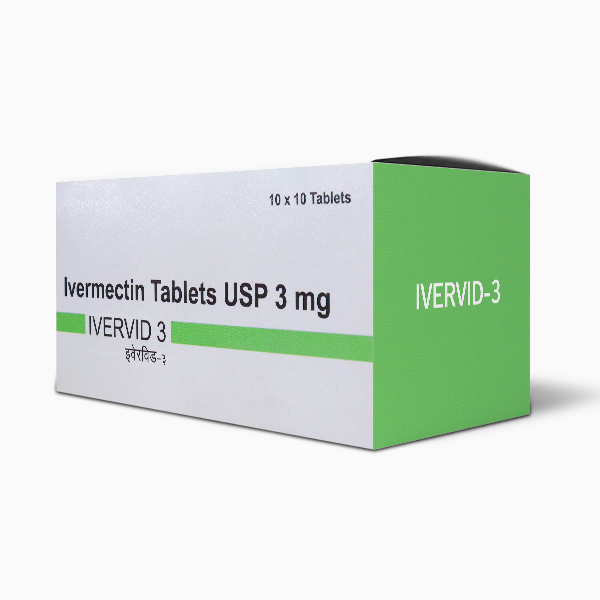
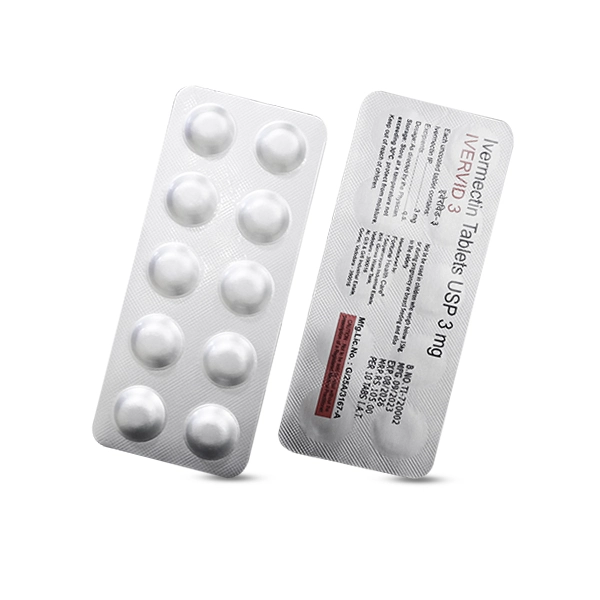
| Packaging Type | Blister |
| Pack Size | 10*10 |
| Dosage | 3 mg |
| Therapeutic class | Antiparasitic agent |
| Action Class | Ectoparasiticides |
| Chemical class | Macrocyclic lactone |
| Manufacturer | Kachhela Medex |
| Shelf Life | 2-3 years from the date of manufacturing |
| Usages | Treats parasitic infections (e.g., strongyloidiasis, onchocerciasis, scabies) |
| Country of Origin | India |
| Storage | Store at room temperature (15-25°C) away from moisture and direct sunlight. |
How does Ivervid 3mg work?
- Ivermectin binds to glutamate-gated chloride ion channels in parasite nerve and muscle cells, increasing chloride ion permeability that leads to hyperpolarization and paralysis and ultimately leads to the death of the parasite.
- Increased Permeability: The binding increases cell membrane permeability to chloride ions, causing the cell to take in chloride ions.
- Hyperpolarization: The heightened influx of chloride ions hyperpolarizes the cell membrane, making it challenging for the parasite’s nerves and muscles to function.
- Paralysis and Death: The parasite’s failure to operate adequately causes paralysis and eventually death.
Usage of Ivervid 3mg
- Treatment of Strongyloidiasis (intestinal roundworm infection).
- It is also used to treat Onchocerciasis (river blindness).
- Scabies skin infestation.
- Lymphatic filariasis (combination with other drugs).
- Head lice and other ectoparasitic infections.
Dosage of Ivervid 3mg
- Single oral dose of 150-200 mcg/kg body weight (e.g., 1 tablet of 3 mg for 25-35 kg weight) taken on an empty stomach with water.
- Strongyloidiasis: 200 mcg/kg single dose.
- Onchocerciasis: 150 mcg/kg single dose (repeat every 6-12 months).
- Scabies: 200 mcg/kg single dose (repeat in 1-2 weeks).
Strength of Medication
Side Effects of Ivervid 3mg
- Nausea,
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Mild skin rash
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Fever
- Lymph node swelling
Interactions
- Blood thinners: Ivermectin can enhance the risk of bleeding when co-administered with blood thinners like warfarin.
- Certain antibiotics: Ivermectin can interact with some antibiotics like azithromycin or clarithromycin, perhaps heightening the risk of adverse effects.
- Anticonvulsants: Ivermectin can interact with anticonvulsants like valproic acid, perhaps altering its effectiveness or heightening the risk of adverse effects.
- Other drugs: Ivermectin has the potential to interact with other drugs, such as some antifungals, antivirals, and anti-anxiety drugs.
- CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin) increase ivermectin levels.
- Barbiturates and benzodiazepines additive CNS depressant effects.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Well absorbed within 30-60 minutes following oral administration.
- Distribution: Widely distributed to tissues (including fat and liver).
- Metabolism: Minimal hepatic metabolism via CYP3A4.
- Elimination: Primarily fecal is approx. (80-90%) With minimal renal excretion.
- Half-life: 12–36 hours (single dose).
Pharmacokinetic Factors Influencing Ivermectin
- Food: Some food may influence the absorption of ivermectin and may enhance its bioavailability for example high-fat food, grape juice, alcohol and caffeine.
- Age: The pharmacokinetics of ivermectin can be influenced by age.
- Liver function: Ivermectin is widely metabolized by the liver, therefore liver impairment may influence its pharmacokinetics.
- Other health conditions: Some health states, like renal disease, can influence the elimination of ivermectin.
Precautions
- Inform your doctor or healthcare professional prior about your medical conditions like heart, kidney or Liver condition.
- Ivervid 3mg may interact with other medications, including warfarin, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and anti-seizure drugs.
- Avoid alcohol while taking Ivervid 3mg tablet.
Conclusion
Ivervid 3 mg is an effective medication against various parasitic infections like onchocerciasis, strongyloidiasis, scabies, and lice. This belongs to the class of Anthelmintics. The drug acts by paralyzing and killing parasites through glutamate-gated chloride ion channel agonism. Proper dosage and precautions are necessary to minimize the side effects and ensure safety.
FAQs
1) What is Ivervid 3 mg used for?
Ivervid 3mg is indicated for the treatment of onchocerciasis, strongyloidiasis, scabies, and infestation caused by lice.
2) How does Ivervid 3 mg function?
Ivervid 3mg medicines functions by paralyzing as well as killing parasites and bringing effective relief against parasitic infections.
3) What are the side effects of Ivervid 3 mg?
Headache, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, and skin rash are common side effects of Ivervid 3mg.
4) How should Ivervid 3 mg be taken?
Ivervid 3mg should be taken in a single dose on an empty stomach with water, at least 1 hour prior to a meal.
5) Does Ivervid 3 mg shows any interaction?
Yes, it interacts with antibiotics like azithromycin or clarithromycin, blood thinners, and Anticonvulsants.
6) Is Ivervid 3 mg safe for everyone?
Yes, Ivervid 3 mg is considered to be safe, but it is recommended to use after consulting a medical professional or doctor.
References
| ivervid-3mg | 30 Tablets $33, 50 Tablets $50, 100 Tablets $90, 200 Tablets $160, 300 Tablets $210 |
|---|
1 review for Ivervid 3mg
It is highly recommended to consult a healthcare provider or doctor before using any of the above medications. This content is for educational purposes only. We advise you to read all the information mentioned by the manufacturer on the medicine before using it.



Zoe Martinez –
Always delivers.