Doxycycline is an antibiotic drug that is employed in the treatment of numerous bacterial infections, such as acne and inflammation caused by bacteria, respiratory infections like Pneumonia and Bronchitis, skin infections like Cellulitis and Abscesses, urinary tract infections, and sexually transmitted diseases like Chlamydia and Gonorrhea.
Key Features:
|
About |
|
|
Drug Class |
Tetracycline |
|
Components |
Doxycycline hydrochloride and inactive ingredients like Fillers, Blinders, and Lubricants. |
|
Uses |
For the treatment of Bacterial infection. |
|
Effective Against |
Gram positive bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae. Gram negative bacteria: Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae. Atypical bacteria: Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae. |
Medications that contain Tadalafil as an active ingredient
Medication | Active ingredients | Dosage | Duration of Action | Uses |
Doxycin 100 mg | Doxycycline | 100 mg | 1-2 weeks | Treat bacterial infection |
Doxycycline 100 mg | Doxycycline | 100 mg | 1-2 weeks | Treat bacterial infection |
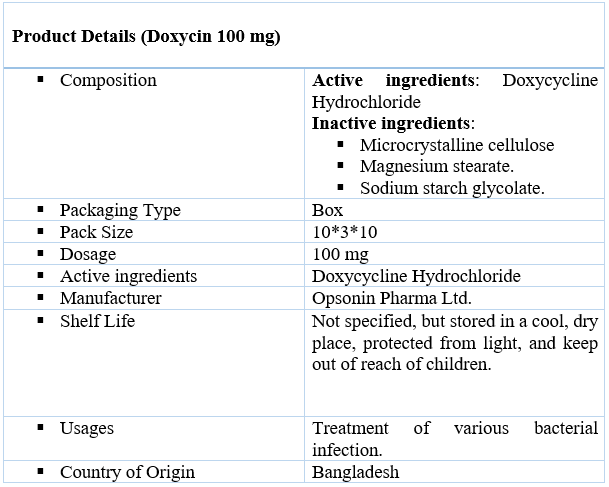
Doxycin 100 mg
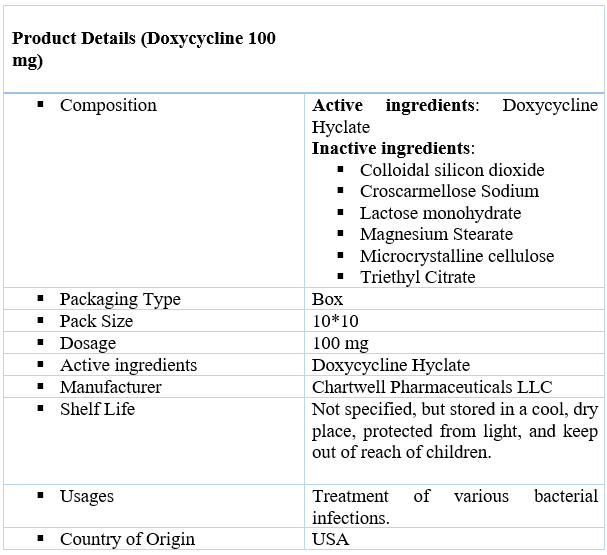
Doxycycline 100 mg
How does Doxycycline work?
- Protein synthesis inhibition: Doxycycline inhibits the bacterial ribosome from producing proteins required for bacterial growth and survival.
- Inhibiting bacterial growth: Through the inhibition of protein synthesis, doxycycline succeeds in inhibiting the growth and proliferation of bacteria, eventually causing them to die.
- Anti-inflammatory activity: In addition to its antibacterial activity, doxycycline has anti-inflammatory activity as well, which will reduce inflammation and tissue injury due to bacterial infection.
Doxycycline Hyclate is an active component of Doxycycline, which is a semi-synthetic derivative of tetracycline. It includes:
- Doxycycline hydrochloride: the salt form of doxycycline.
- Inactive ingredients: Microcrystalline cellulose, Magnesium stearate, Sodium starch glycolate, Colloidal silicon dioxide, Lactose monohydrate,
Doxycycline is used to treat various bacterial infections:
- Respiratory tract infections, Pneumonia, Bronchitis, Sinusitis.
- Skin infections like Acne, Cellulitis, and Abscesses.
- Sexually transmitted infections like Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis.
- Malaria
- Periodontal disease
- Rosacea
- Urinary tract infections
- Gastrointestinal infections
Interaction
Doxycycline may interact with other medications, substances, and foods such as:
- Antacids: aluminium, calcium, or magnesium-containing antacids, which lower the absorption of doxycycline.
- Iron supplements: lower the absorption of doxycycline.
- Blood thinners: warfarin, for example, can elevate the risk of bleeding.
- Retinoids: those for use in acne or other skin diseases, which can elevate sunburn risk.
- Certain antibiotics, for example, penicillin, can reduce the effectiveness of doxycycline.
- Foods: dairy foods, calcium-containing foods, and iron-containing foods may reduce doxycycline absorption.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics is the study of the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME)
- Doxycycline is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with a bioavailability of approximately 70-80%. Food can affect absorption, but the impact is generally minimal.
- Doxycycline is widely distributed throughout the body, with high tissue and fluid concentrations, including:
- Tissues: liver, kidney, lung, and skin
- Fluids: bile, urine, and saliva
- Lipophilicity: facilitates good intracellular and tissue penetration
- Doxycycline is minimally metabolized in the body, with most metabolism occurring in the liver, and some inactive metabolites are produced.
- Doxycycline is mainly eliminated in the:
- Bile: large amounts are removed through the bile into the faeces.
- Urine: smaller quantities are removed through the kidneys into the urine
- Half-life: around 18-22 hours, making it possible to give once- or twice-daily
These pharmacokinetic features add to the efficacy and convenience of doxycycline in the treatment of most bacterial infections.
Clinical Trials
Doxycycline has been investigated in numerous clinical trials for a range of ailments, including:
- Cancer Treatment
Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: Doxycycline’s efficacy was studied in a phase 2 trial for the induction of metakaryotic cell death from primary pancreatic tumors. The trial determined that doxycycline can kill eukaryotic and metakaryotic cells, which may reduce cancer relapse and metastases.
- Infectious Diseases
- COVID-19: The randomized controlled trial in India showed that doxycycline reduces the need for ICU admission in hospitalized COVID-19 The trial speculated that the anti-inflammatory effect of doxycycline might be behind the benefits.
- Scrub Typhus: Combination therapy with intravenous doxycycline and azithromycin is a better choice compared to either drug as monotherapy in severe scrub typhus, according to a trial.
- Other Conditions
- Diabetic Retinopathy: A trial evaluated the efficacy of doxycycline versus placebo in the treatment of severe non-proliferative or mild or moderate proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: One single-centre randomized open-label study compared the efficacy of doxycycline as combination therapy with methotrexate for active rheumatoid arthritis.
- Syphilitic Uveitis: One retrospective cohort study indicated that oral doxycycline produced clinical and serologic responses comparable to IV penicillin.
Side effects
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
- Vaginal yeast infection
- Allergic manifestations such as hives, rashes, and itching
Precautions
- Doxycycline is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation.
- The drug is not indicated in children below 8 years old.
- Inform the doctor about existing medical conditions such as the kidneys, liver, or heart.
Conclusion
Doxycycline is a versatile and powerful antibiotic with a large role to play in treating several bacterial infections. It is a useful drug of therapy for a variety of ailments such as respiratory infection, cutaneous infection, and sexually transmitted diseases. By doing this, patients can benefit from the healing effects of doxycycline without increasing the threat of drug allergy.
References
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7048645/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555888/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556599/
FAQs
- For what is doxycycline used?
Doxycycline is used to treat various bacterial infections like Pneumonia, Bronchitis, Sinusitis, Cellulitis, Abscesses, Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis.
- Can doxycycline be used for viral infections?
No, doxycycline is effective only against bacterial infections.
- Can I take doxycycline with food?
Yes, doxycycline can be taken with or without food, but avoid taking it with dairy products or antacids.
- How long does it take for doxycycline to work?
It takes almost 1-2 weeks.
- What are the common side effects of doxycycline?
The common side effects of doxycycline are dizziness, headache, and Fatigue.