-
-
Fenbendazole Capsules 444 mg
$42.00 – $300.00Price range: $42.00 through $300.00Rated 4.00 out of 5 -
Wormchrist 444mg fenbendazole
$42.00 – $300.00Price range: $42.00 through $300.00Rated 5.00 out of 5 -
Pure Fenbentoro capsules 222 mg
$42.00 – $300.00Price range: $42.00 through $300.00Rated 4.50 out of 5 -
Fenbendazole Capsules 500 mg
$42.00 – $300.00Price range: $42.00 through $300.00Rated 4.50 out of 5 -
-
-
-
-
-
Mebex 100 MG Mebendazole Tablet
$50.00 – $290.00Price range: $50.00 through $290.00Rated 5.00 out of 5 -
-
-
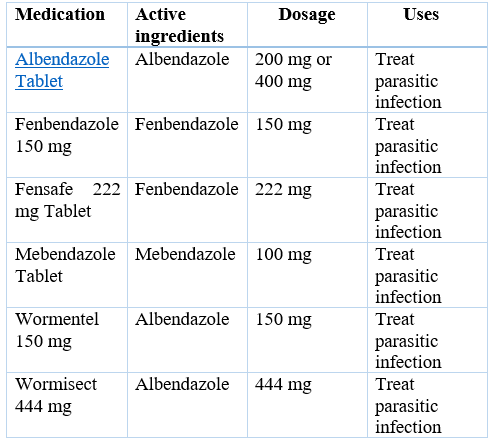
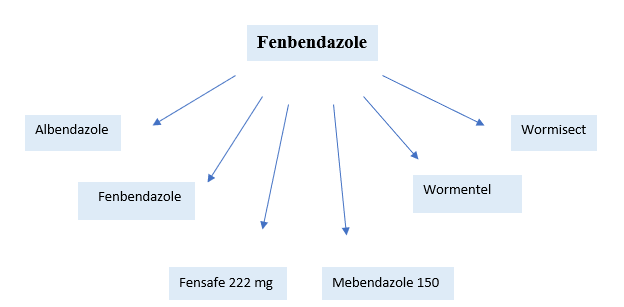
Fenbendazole is a medication that is formulated to treat various parasitic infections caused by hookworms, whipworms, strongyles, Cestodes (tapeworm), and other parasites like Giardia and certain protozoa. This antiparasitic medication belongs to benzimidazole class of drug. It is specifically used in veterinary medicine to treat various worm infections in animals. Fenbendazole is a benzimidazole derivative with antiparasitic activity, which is distinguished by substitutions in positions 2 and 5 by (methoxycarbonyl) amino groups and phenylsulfanediyl groups. It is an anthelmintic of broad spectrum used in veterinary medicine to treat nematodal diseases and is an anti-nematodal medication.
Key Features:

How does Fenbendazole works?
Fenbendazole is an antiparasitic drug that acts by:
- Preventing microtubule formation: Fenbendazole inhibits tubulin, a protein needed for microtubule formation, which interferes with cellular processes in parasites.
- Disrupting glucose uptake: It inhibits glucose uptake, depriving parasites of energy and nutrients.
- Injuring parasite cells: Fenbendazole induces cellular damage, eventually causing the death of the parasites.
Fenbendazole kills many parasites, such as:
- Hookworms
- Roundworms
- Whipworms
- Tapeworms
It’s widely used in veterinary medicine and has also been investigated for possible use in human health. It’s not always approved for use in humans, and additional studies are required to know for certain about its effectiveness and safety in humans. Consult a healthcare professional for specific recommendations.
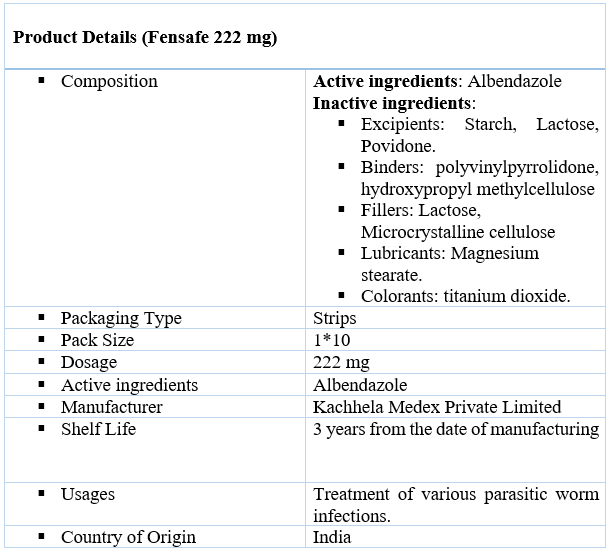
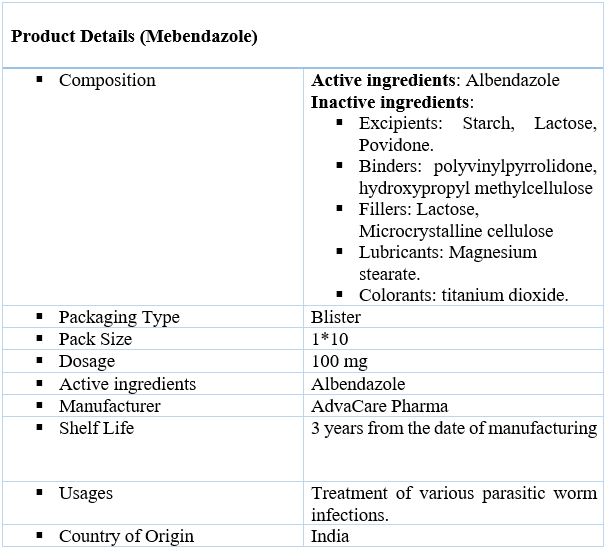
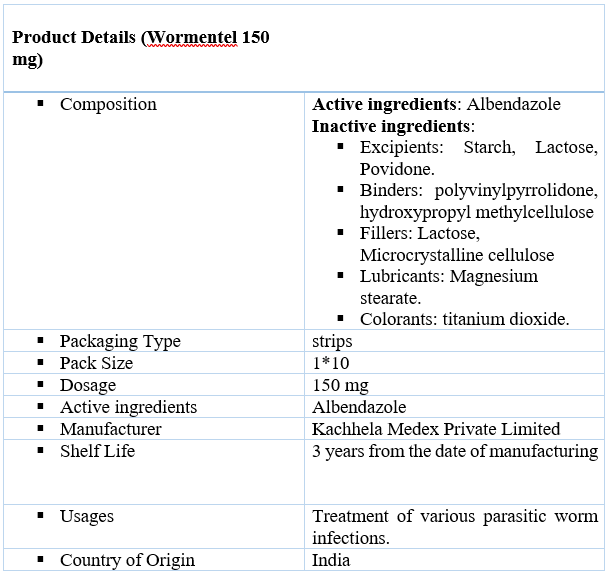
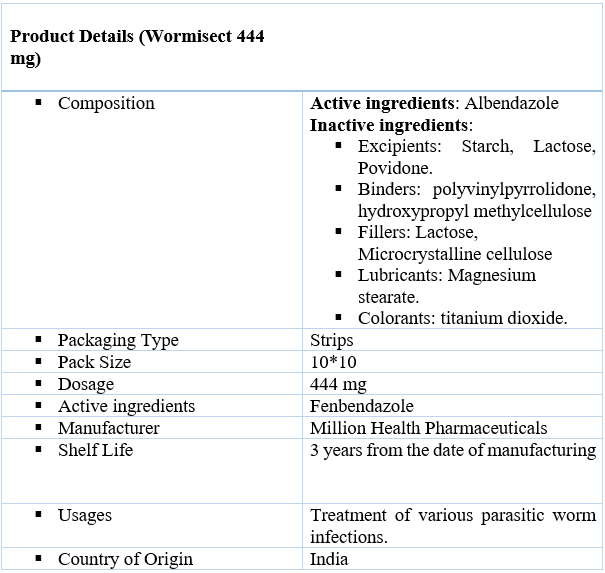
Uses
Fenbendazole is utilized for treating parasitic infestations in multiple animal species, including:
- Companion animals: dogs, cats, and other companion animals
- Livestock: cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, and horses
- Poultry: chickens, turkeys, and other poultry
Fenbendazole comes in different forms, including:
- Tablets: oral tablets for dogs, cats, and other animals
- Suspensions: liquid suspensions for oral use
- Pastes: paste preparations for horses and other large animal species
- Feed additives: medicated feeds for poultry and livestock
Dosage
Fenbendazole dosage is based on the parasite type, animal species, and product formulation. Always use the recommended dosage and administration method as indicated by the manufacturer or veterinarian.
Interactions
Fenbendazole has the potential to interact with other drugs, including:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
- Some antibiotics
- Other antiparasitic drugs
Do not administer Fenbendazole along with other medications without consulting a veterinarian or healthcare provider.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Fenbendazole are usually mild and could include:
- Gastrointestinal disturbance (vomiting, diarrhea, nausea)
- Lack of appetite
- Lethargy
Serious side effects but only rarely occur, particularly with long-term administration or in high doses. Inform a veterinarian or healthcare provider if any unusual signs appear.
Precautions
- Fenbendazole is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation.
- The drug is not indicated in children below 8 years old.
- Inform the doctor about existing medical conditions such as the kidneys, liver, or heart.
Conclusion
Fenbendazole is a potent antiparasitic drug used for the treatment of many parasitic infections in animals. But ensure to use it in the recommended dosage, check for side effects, and take advice from a veterinarian or medical professional.
References
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30093705/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37998737/
FAQs
- What is Fenbendazole used for?
Fenbendazole is utilized to treat parasitic infections in animals such as hookworms, roundworms, whipworms, and tapeworms.
- Is Fenbendazole safe for humans?
Fenbendazole isn’t always approved for use in humans, and its efficacy and safety in humans are currently under study.
- Can Fenbendazole be used in pregnant animals?
Fenbendazole should only be used with care in pregnant animals, and only under the advice of a veterinarian.
- What are the side effects of Fenbendazole?
Side effects are usually gastrointestinal upset, lethargy, and loss of appetite. Serious but uncommon side effects may present, particularly with high dosing or long-term use.