Sepsis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
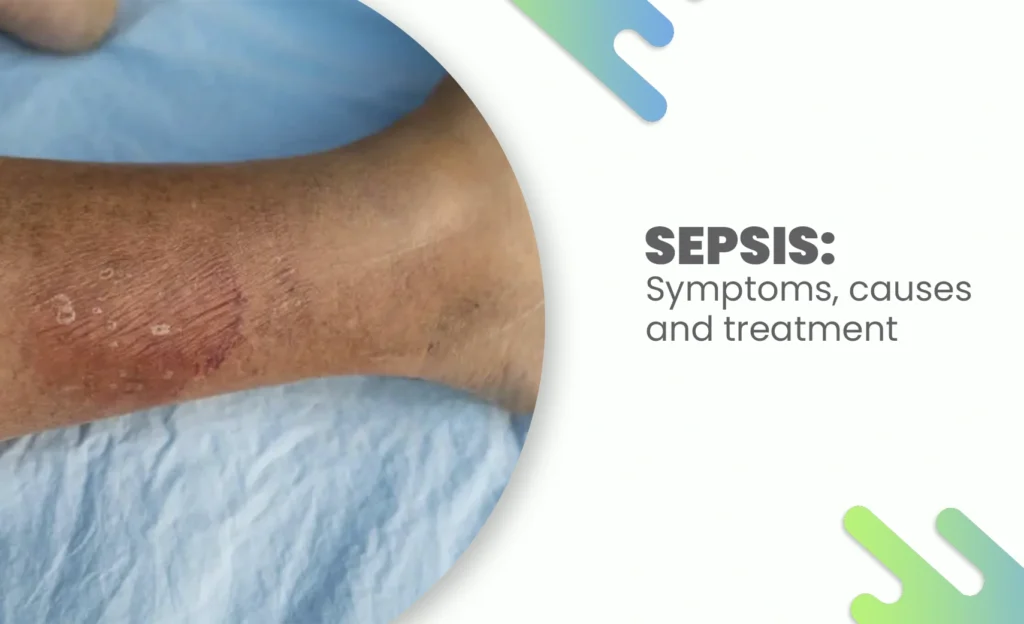
Let’s be real for a second, the word sepsis doesn’t get nearly as much attention as it deserves. It’s one of those silent medical emergencies that most people don’t think about until it’s too late. Unlike a broken bone or a visible injury, sepsis hides in plain sight often beginning as something harmless like a simple infection or even a mild fever. But behind the scenes, the body is waging war against itself.
I remember interviewing an ICU nurse a few years ago who said something that stuck with me: “Sepsis doesn’t knock on the door; it kicks it down.” And honestly, that’s the best way to describe it.
What Is Sepsis, Really?
In plain terms, sepsis is your body’s extreme, life-threatening reaction to an infection. Normally, your immune system fights infections to protect you. But with sepsis, that protective response goes haywire. Instead of fighting the infection, it starts damaging your own tissues and organs.
You might think of it like a smoke detector that goes off not just when there’s smoke in the kitchen but when someone lights a candle in the living room. The alarm system overreacts and chaos follows.
Sepsis can stem from any infection, bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic. Urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and skin infections are among the most common culprits. Even a minor cut or an infected tooth can spiral into sepsis if things go wrong.
Early Signs and Symptoms
Here’s the tricky part, early sepsis can look like the flu, food poisoning, or even exhaustion. You might feel feverish, weak, or confused. But when those signs escalate fast, it’s often a red flag.
Common symptoms include:
- Fever or low body temperature
- Rapid heartbeat
- Fast breathing
- Extreme fatigue
- Confusion or disorientation
- Chills, clammy skin, or pale complexion
Some people also experience nausea, diarrhea, or severe muscle pain, making it hard to pinpoint what’s really going on.
Interestingly, many survivors say they “just knew something was wrong”, like a gut feeling that their illness felt different. That intuition often ends up saving lives.
What Causes Sepsis?
The causes aren’t always dramatic. Sometimes, it’s a wound that doesn’t heal properly. Other times, it’s a bacterial infection that spreads from one part of the body to another.
Let’s break this down simply.
When bacteria (or other pathogens) invade the body, your immune system releases chemicals into the bloodstream to fight them. In sepsis, this immune response becomes uncontrolled. The chemicals trigger widespread inflammation, blood clots, and leaky blood vessels which can slow oxygen flow to organs.
If left untreated, this cascade can lead to septic shock, a severe drop in blood pressure that can be fatal.
Now, while antibiotics are the cornerstone of sepsis treatment, preventing infections in the first place is just as crucial. That’s where overall infection control and hygiene matter — including regular handwashing, wound care, and early treatment of infections.
And speaking of infection control, it’s worth mentioning that in some parts of the world, medications like Iverheal 12mg are used for parasitic infections that, if neglected, can lead to serious complications and even trigger sepsis-like symptoms. It’s not a treatment for sepsis itself, but it plays a vital role in preventing the kind of severe infections that sometimes spiral into systemic inflammation.
Who’s Most at Risk?
Anyone can get sepsis, but some groups are more vulnerable than others.
Older adults, newborns, and people with weakened immune systems (like cancer patients or those with chronic diseases) are especially at risk. Individuals with diabetes, kidney disease, or those recovering from major surgery also fall into this category.
To be honest, even healthy individuals aren’t completely safe. Something as small as a skin infection after a burn or insect bite can sometimes set off the chain reaction leading to sepsis.
It’s not as simple as saying “only sick people get sepsis.” The truth is, the human immune system is complex and sometimes, it just overreacts.
The Role of Infections – and Why Prevention Matters
Here’s the thing, preventing sepsis isn’t about living in fear of bacteria. It’s about understanding how infections spread and how to manage them early.
For example, gastrointestinal infections or parasitic infestations often ignored, can weaken your system over time. Some of these infections, if untreated, can create secondary bacterial infections that push your immune system into overdrive.
That’s why medications like Iverheal 12mg are prescribed in specific cases. They help eliminate parasites that might otherwise linger and cause systemic issues. By clearing these infections, you’re essentially stopping one domino from toppling the next.
I once spoke to a traveler who returned from Southeast Asia with what he thought was a simple stomach bug. Weeks later, it turned out to be a parasitic infection that nearly triggered sepsis. After treatment, which included antiparasitic medication similar to Iverheal 12mg, he recovered fully. His takeaway was simple but powerful: never underestimate an infection, no matter how small it seems.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Spot Sepsis
Diagnosing sepsis isn’t always straightforward. Doctors usually run a combination of tests of blood cultures to identify bacteria, imaging scans to find the source of infection, and blood tests to check organ function.
Because sepsis can progress rapidly, time is everything. The “golden hour” the first few hours after onset can literally mean the difference between life and death.
That said, modern medicine has made huge strides in improving outcomes. Rapid diagnostic tools and awareness campaigns have helped hospitals identify and treat sepsis earlier than ever before.
Treatment: Fighting Back Against Sepsis
Treatment usually begins in a hospital setting, often the ICU. The primary goals are to control the infection, support organ function, and stabilize blood pressure.
Antibiotics are given immediately (sometimes even before test results come back), along with fluids to prevent dehydration and maintain circulation. In severe cases, patients may need oxygen therapy, dialysis, or surgery to remove the source of infection.
In certain regions, when sepsis is linked to parasitic or mixed infections, antiparasitic medications such as Iverheal 12mg might be part of a broader protocol to target the root cause. Again, it’s important to clarify that Iverheal 12mg is not a sepsis cure, but addressing the infection behind it can be lifesaving.
Recovery can take weeks or even months. Some survivors face what’s called post-sepsis syndrome lingering fatigue, memory issues, and anxiety long after the infection clears.
What It Feels Like – A Human Perspective
I once met a woman named Sarah who developed sepsis after a routine dental procedure. At first, she thought she was just catching a cold fever, chills, and general fatigue. Within 24 hours, she was in the ICU. She told me later that what scared her most wasn’t the pain, but how fast everything happened.
“I remember sitting on my couch one minute and waking up surrounded by doctors the next,” she said. “It felt like my body just shut down.”
That story isn’t unique. Thousands of people every year experience something similar and not all survive. The CDC estimates that about 1.7 million adults in the U.S. develop sepsis annually, and roughly 350,000 die from it. Those are sobering numbers.
Can You Prevent Sepsis?
While not every case is preventable, there are clear steps to reduce your risk:
- Treat infections early. Don’t ignore fever, swelling, or wounds that don’t heal.
- Stay up to date on vaccines. Especially against flu and pneumonia.
- Maintain hygiene. Wash hands, clean wounds, and avoid sharing personal items.
- Take prescribed medications correctly. Whether it’s antibiotics or antiparasitic drugs like Iverheal 12mg, complete the full course. Stopping early can cause reinfection or resistance.
- Monitor chronic conditions. If you have diabetes or heart disease, keeping them under control can lower your immunity.
Sometimes, prevention looks like boring handwashing, clean bandages, and timely checkups. But those simple habits can literally save your life.
The Hidden Link Between Global Infections and Sepsis
In many developing regions, parasitic infections are still rampant. Intestinal worms, filarial infections, and even skin parasites can cause long-term inflammation. While these might sound far removed from sepsis, they weaken the immune system and increase vulnerability to bacterial invasion.
In that context, medications like Iverheal 12mg have a bigger role not in treating sepsis itself, but in keeping infection levels low and preventing systemic complications. It’s a reminder that global health is interconnected. Preventing one kind of infection helps protect against another.
Interestingly, some research has shown that people who regularly undergo deworming or preventive antiparasitic treatments in endemic areas report fewer severe systemic infections. It’s one of those small but crucial public health interventions that quietly save lives.
Living After Sepsis
Surviving sepsis can feel like being given a second chance. But recovery isn’t just physical, it’s deeply emotional too. Many survivors talk about lingering anxiety or PTSD, especially after long ICU stays.
Rebuilding strength takes patience. Nutrition, physical therapy, and mental health support all play a role. Family education is just as important because understanding what happened helps prevent it from happening again.
That said, awareness is key. If more people understood how quickly a minor infection could become a medical emergency, far fewer would ignore those first warning signs.
Final Thoughts
Sepsis isn’t some obscure medical condition, it’s a global health threat that touches millions every year. The tragedy is that many cases start small: a UTI, a sore throat, a small abscess.
But awareness and early action can turn the tide. Knowing when to seek help, finishing your medication, and keeping infections under control can make all the difference.
Medications like Iverheal 12mg remind us that infection management isn’t just about one disease it’s about protecting the body’s balance as a whole. From parasites to bacteria, from prevention to recovery, every layer matters.
So, the next time you or someone you know brushes off an infection as “nothing serious,” remember this: sometimes the smallest spark can light the biggest fire.
FAQs
- Can sepsis start from a small infection?
Yes and that’s what makes it so dangerous. Even a mild infection, like a UTI or an infected cut, can trigger sepsis if it spreads or isn’t treated early. The body’s immune system can go into overdrive, damaging its own tissues in the process. So, it’s always worth paying attention to persistent or worsening symptoms. - How fast does sepsis develop?
It varies, but sepsis can progress shockingly fast sometimes within hours. That’s why early detection is everything. If you notice fever, confusion, rapid heartbeat, or difficulty breathing after an infection, don’t wait it out. Get medical help immediately. - Is sepsis contagious?
No, sepsis itself isn’t contagious. You can’t “catch” sepsis from someone else. However, the underlying infection (like a bacterial or viral infection) that caused sepsis may be contagious in some cases. Good hygiene and infection control are still essential. - Can medications like Iverheal 12mg help prevent sepsis?
Not directly, Iverheal 12mg isn’t a treatment for sepsis. But it can help control parasitic infections that, if ignored, might weaken the immune system and increase infection risk. In that sense, managing infections early with the right medications helps reduce the chance of severe complications like sepsis. - What’s recovery like after sepsis?
Recovery can take time. Many survivors feel weak or mentally foggy for weeks or months. Doctors call it post-sepsis syndrome. With the right care, good nutrition, rest, and sometimes physical therapy most people gradually regain their strength. Emotional recovery matters too, since the experience can be quite traumatic.