Cephalexin is a widely used first generation oral cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat many common bacterial infections of the skin, ear, throat, respiratory tract and urinary tract. It’s generally well tolerated, prescribed by clinicians around the world, and comes in capsules, tablets and an oral suspension for children.
What is cephalexin and how it works
Cephalexin belongs to the cephalosporin family of beta-lactam antibiotics. It works by interfering with bacterial cell-wall synthesis, which ultimately kills susceptible bacteria or stops their growth. Because of this mechanism it is effective against many common gram-positive organisms (for example Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species) and some gram-negative bacteria. Cephalexin is not effective against viral infections.
Common uses / clinical indications
Clinicians commonly prescribe cephalexin for infections such as:
- Skin and soft-tissue infections (non-MRSA cellulitis, impetigo).
- Upper and lower respiratory tract infections (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, uncomplicated pneumonia in appropriate settings).
- Otitis media (middle ear infection) in children.
- Uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
- Prophylaxis in selected minor surgical procedures when recommended by guidelines.
Typical dosing (general guidance — individual dosing varies)
Dosing depends on the infection type, severity, patient age and kidney function. Common adult regimens often range from 250 mg to 1,000 mg daily, divided into two to four doses; many outpatient infections are treated with 250–500 mg every 6–12 hours. Pediatric dosing is weight-based (commonly 25–50 mg/kg/day divided into 2–4 doses; higher ranges used for otitis media). In renal impairment doses must be adjusted. Always follow the prescribing clinician’s directions or local formularies.
Safety, common side effects and important warnings
Most people tolerate cephalexin well. Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) and rash. Serious but uncommon adverse events include allergic reactions (including anaphylaxis in rare cases for those with cephalosporin or penicillin sensitivity), antibiotic-associated colitis (including C. difficile), blood dyscrasias and liver enzyme changes. If severe diarrhea, jaundice, unexplained bruising, or signs of allergic reaction occur, seek immediate medical care. Avoid use if you have a known severe allergy to cephalosporins.
Drug interactions and precautions
Cephalexin has relatively few clinically important drug interactions, but clinicians check concomitant medicines and comorbidities before prescribing. Renal function affects excretion, dose adjustments may be needed for kidney impairment. Also tell your provider about any history of penicillin allergy (cross-reactivity is possible but not universal) and about pregnancy or breastfeeding; cephalexin is often used in pregnancy when clinically indicated, but that decision should be made by a clinician.
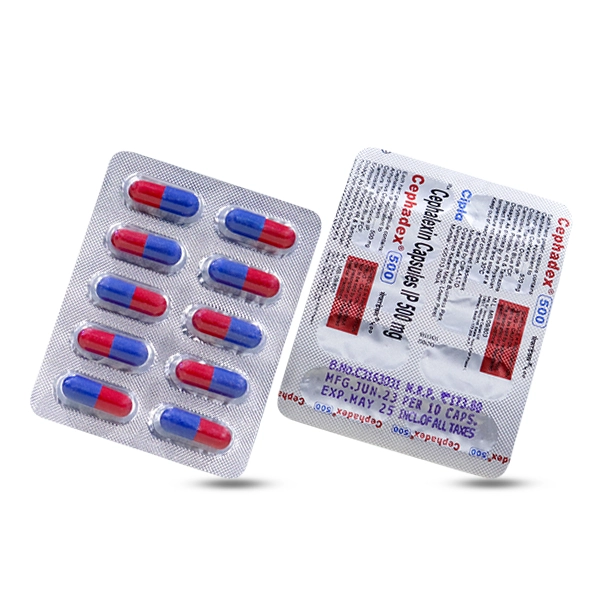
Formulations & the Cephadex products
We offer two widely available strengths of cephalexin:
- Cephadex 250 mg — oral capsule/tablet (typical use: mild-to-moderate infections, pediatric dosing by fraction or using an oral suspension when available).
- Cephadex 500 mg — oral capsule/tablet (typical use: moderate infections or where a larger per-dose amount is clinically appropriate).
Both strengths contain the same active ingredient (cephalexin). The strength prescribed depends on infection type, patient age/weight and clinician judgment. Packaging, excipients and local availability may differ by manufacturer and country — always check the product label and dispensing information.
Practical advice for patients
- Take the full course as prescribed even if you feel better earlier — stopping early can lead to relapse or resistance.
- With or without food: cephalexin may be taken with food to reduce stomach upset; absorption is generally reliable either way.
- Missed dose: take as soon as you remember, but do not double doses.
- Store as instructed on the label; liquid suspensions may have refrigeration recommendations.
- Report severe diarrhea, rash, yellowing of skin/eyes, or severe allergic symptoms promptly.
Evidence & effectiveness
Cephalexin’s pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy and safety have been extensively studied; modern systematic reviews and pharmacokinetic studies summarize its predictable absorption and renal excretion, making it a reliable choice for many outpatient infections when the causative organism is susceptible. Emerging evidence and guideline updates (for example on optimal dosing frequency for increased adherence) continue to refine how clinicians use the drug. Decisions should follow local resistance patterns and official guidelines.
Final note & medical disclaimer
This data is for informational purposes to describe the antibiotic cephalexin and the listed products (Cephadex 250 mg and Cephadex 500 mg). It is not medical advice. Always consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis, personalized dosing and to confirm that cephalexin is appropriate for your condition.